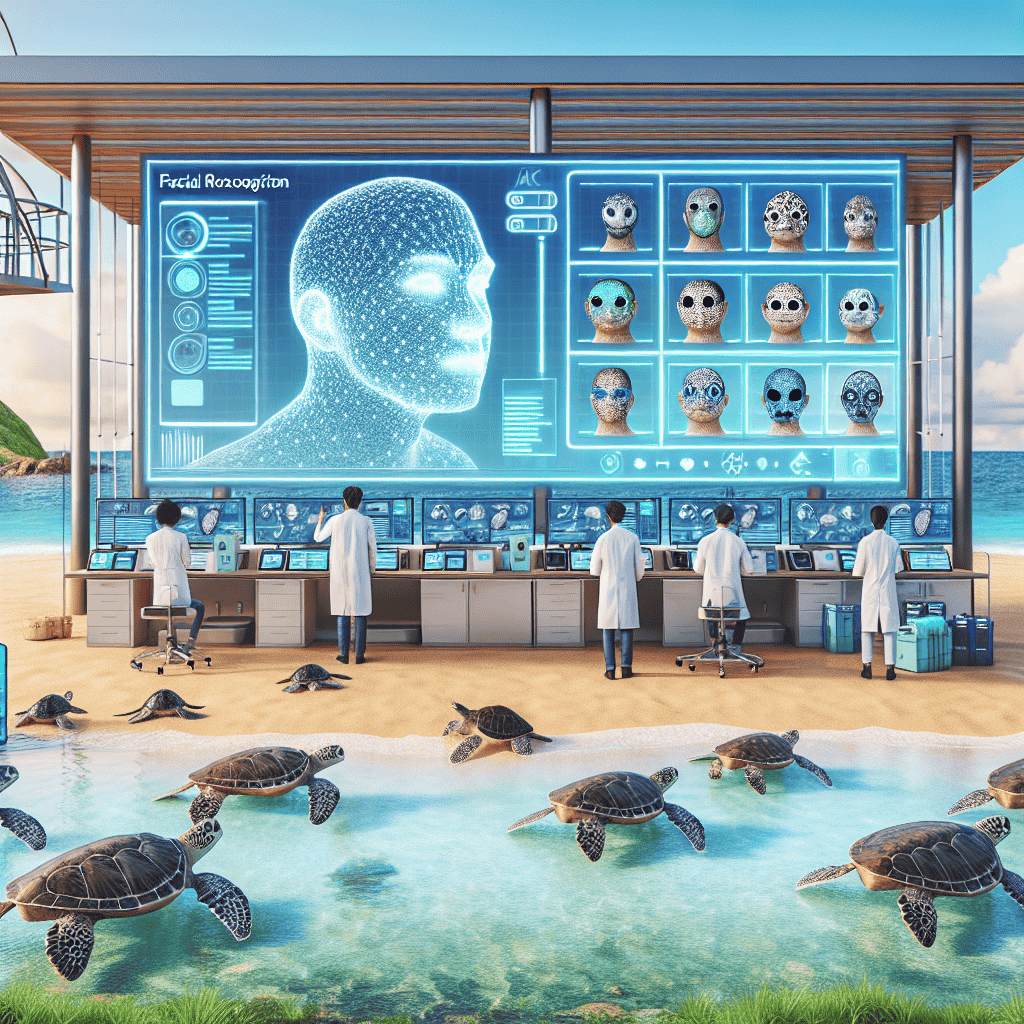
Enhancing Turtle Conservation through AI Facial Recognition Technology involves leveraging advanced machine learning algorithms to identify and monitor individual turtles based on unique facial patterns. This innovative approach addresses the challenges of traditional tagging methods, which can be invasive and labor-intensive. By utilizing AI-driven facial recognition, researchers can efficiently track turtle populations, assess health, and study migratory patterns with minimal disturbance to the animals. This technology not only improves data accuracy and collection speed but also aids in the development of targeted conservation strategies, ultimately contributing to the preservation of these vital marine species and their ecosystems.
Integrating AI Facial Recognition in Turtle Conservation Efforts
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into wildlife conservation has opened new avenues for protecting endangered species, and one of the most promising applications is the use of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation efforts. This innovative approach is transforming how researchers and conservationists monitor and protect turtle populations, offering a more efficient and non-invasive method of tracking individual animals over time. As turtle species around the world face increasing threats from habitat destruction, climate change, and poaching, the need for effective conservation strategies has never been more urgent.
AI facial recognition technology, which has been successfully applied in human identification, is now being adapted to recognize individual turtles based on unique patterns on their shells and faces. This technology leverages machine learning algorithms to analyze images of turtles, identifying distinct features that differentiate one turtle from another. By creating a database of these unique identifiers, researchers can track individual turtles throughout their lives, gaining valuable insights into their behavior, migration patterns, and population dynamics. This data is crucial for developing targeted conservation strategies that address the specific needs of different turtle populations.
One of the primary advantages of using AI facial recognition in turtle conservation is its non-invasive nature. Traditional methods of tracking turtles, such as tagging or attaching GPS devices, can be stressful for the animals and may alter their natural behavior. In contrast, AI facial recognition requires only photographs, which can be taken from a distance without disturbing the turtles. This approach not only minimizes the impact on the animals but also allows for the collection of data from a larger number of individuals, providing a more comprehensive understanding of the population.
Moreover, AI facial recognition technology enhances the efficiency of data collection and analysis. In the past, researchers had to manually identify and catalog individual turtles, a time-consuming and error-prone process. With AI, this task can be automated, allowing for the rapid processing of large volumes of data. This increased efficiency enables conservationists to respond more quickly to changes in turtle populations, such as sudden declines or shifts in migration patterns, and to implement timely conservation measures.
Furthermore, the use of AI in turtle conservation fosters collaboration among researchers, conservation organizations, and local communities. By sharing data and insights through centralized databases, stakeholders can work together to develop and implement effective conservation strategies. This collaborative approach is essential for addressing the complex challenges facing turtle populations, which often span multiple regions and jurisdictions.
In addition to its practical benefits, the integration of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation also raises awareness about the plight of these endangered species. By highlighting the innovative use of technology in conservation efforts, researchers can engage the public and inspire support for turtle protection initiatives. This increased awareness can lead to greater funding and resources for conservation programs, ultimately contributing to the long-term survival of turtle populations.
In conclusion, the application of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation represents a significant advancement in the field of wildlife protection. By providing a non-invasive, efficient, and collaborative approach to monitoring turtle populations, this technology offers new hope for the preservation of these ancient and vulnerable creatures. As AI continues to evolve, its potential to enhance conservation efforts will undoubtedly grow, offering new opportunities to safeguard the planet’s biodiversity for future generations.
The Role of AI in Identifying Individual Turtles for Conservation
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into wildlife conservation efforts has opened new avenues for protecting endangered species. Among these innovative applications, AI facial recognition technology has emerged as a promising tool in the conservation of turtles, a group of reptiles facing numerous threats worldwide. By enabling researchers to identify individual turtles with precision, this technology enhances the ability to monitor populations, track movements, and implement targeted conservation strategies.
Traditionally, identifying individual turtles has been a labor-intensive process, often involving physical tagging or marking. These methods, while effective, can be invasive and stressful for the animals. Moreover, they require significant human resources and can be prone to errors. In contrast, AI facial recognition offers a non-invasive alternative that leverages the unique patterns on a turtle’s face or shell to distinguish one individual from another. This approach not only reduces the need for physical interaction but also increases the accuracy and efficiency of data collection.
The application of AI in turtle conservation begins with the creation of a comprehensive database of images. Researchers capture photographs of turtles in their natural habitats, ensuring that the images are clear and detailed enough for analysis. These images are then fed into an AI system, which uses machine learning algorithms to identify distinctive features and patterns. Over time, the system becomes adept at recognizing individual turtles, even as they grow and their appearances change slightly.
One of the significant advantages of using AI facial recognition in turtle conservation is its ability to process vast amounts of data quickly. This capability is particularly beneficial in large-scale conservation projects where monitoring numerous individuals is essential. By automating the identification process, researchers can allocate more time and resources to other critical aspects of conservation, such as habitat restoration and community engagement.
Furthermore, AI technology facilitates long-term monitoring of turtle populations. By maintaining a digital record of individual turtles, researchers can track their movements, reproductive success, and survival rates over extended periods. This information is invaluable for understanding population dynamics and assessing the effectiveness of conservation interventions. For instance, if a particular nesting site shows a decline in turtle numbers, conservationists can investigate potential causes and implement corrective measures promptly.
In addition to aiding in population monitoring, AI facial recognition can also play a crucial role in combating illegal wildlife trade. By creating a global database of identified turtles, authorities can track and verify the origins of turtles in trade, thereby reducing the risk of poaching and illegal trafficking. This application underscores the broader potential of AI technology in enhancing wildlife law enforcement and ensuring the protection of vulnerable species.
Despite its promise, the implementation of AI facial recognition in turtle conservation is not without challenges. High-quality image collection can be difficult in remote or underwater environments, and the initial development of AI systems requires substantial investment. However, as technology advances and becomes more accessible, these obstacles are likely to diminish, paving the way for wider adoption.
In conclusion, AI facial recognition technology represents a significant advancement in turtle conservation efforts. By providing a non-invasive, efficient, and accurate method for identifying individual turtles, it enhances the ability of researchers to monitor populations and implement effective conservation strategies. As this technology continues to evolve, it holds the potential to transform not only turtle conservation but also the broader field of wildlife protection, offering hope for the preservation of biodiversity in an increasingly threatened world.
How Facial Recognition Technology is Revolutionizing Turtle Research
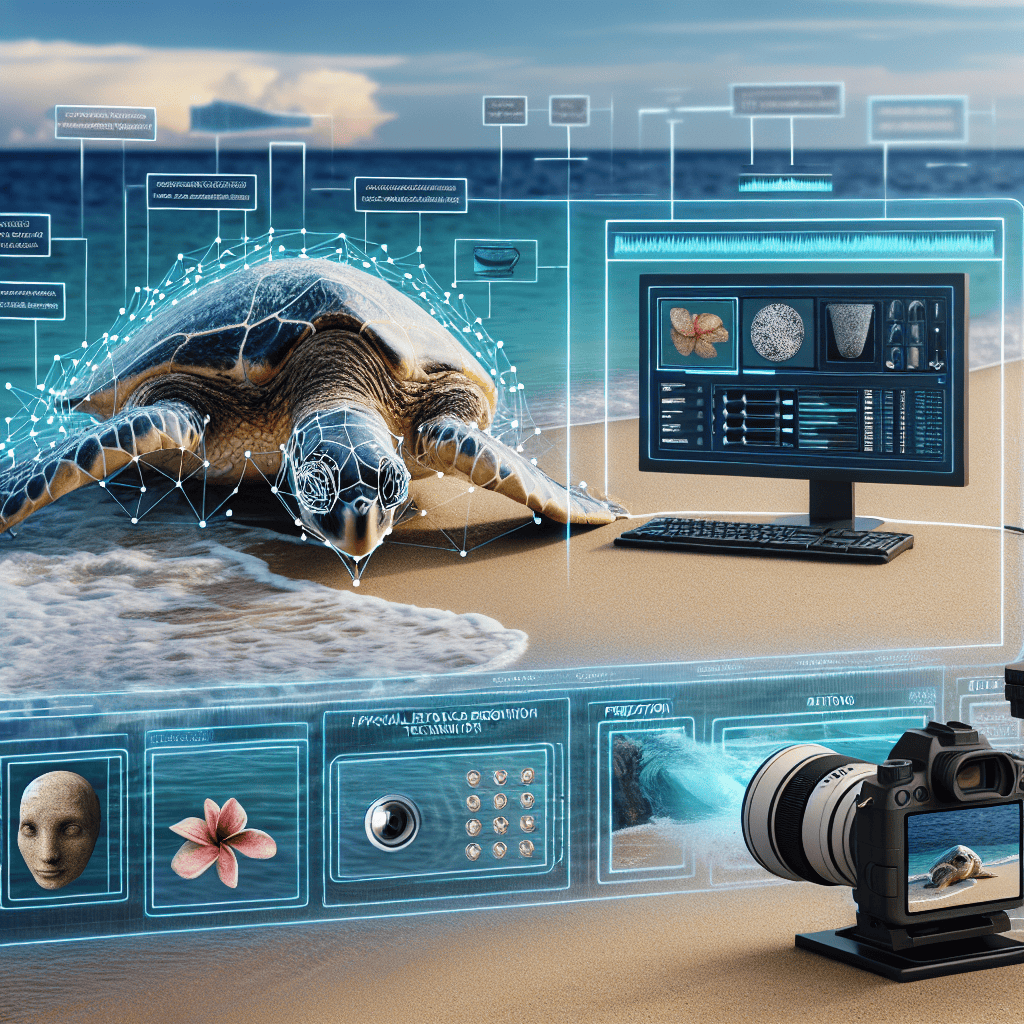
Facial recognition technology, once primarily associated with human identification and security systems, is now making significant strides in the field of wildlife conservation. Among the beneficiaries of this technological advancement are turtles, a group of reptiles that have long been the focus of conservation efforts due to their vulnerable status. The application of artificial intelligence (AI) in facial recognition is revolutionizing turtle research by providing researchers with innovative tools to monitor and protect these ancient creatures more effectively.
Traditionally, turtle conservation has relied on methods such as tagging and manual identification to track individual animals. These methods, while effective to some extent, are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and often stressful for the animals. Moreover, the physical tags can sometimes cause harm or discomfort to the turtles. In contrast, AI-driven facial recognition offers a non-invasive alternative that significantly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of monitoring efforts. By analyzing the unique patterns on a turtle’s face, much like a human fingerprint, researchers can identify individual turtles without the need for physical contact.
The implementation of facial recognition technology in turtle research is facilitated by the development of sophisticated algorithms capable of processing and analyzing vast amounts of visual data. These algorithms are trained to recognize the distinct features of a turtle’s face, such as the arrangement of scales and the shape of the beak. As a result, researchers can quickly and accurately identify individual turtles from photographs or video footage, even in large populations. This capability is particularly valuable in studying migratory patterns, population dynamics, and the health of turtle populations across different habitats.
Furthermore, the integration of AI facial recognition into turtle conservation efforts allows for the collection of longitudinal data, which is crucial for understanding long-term trends and changes in turtle populations. By maintaining a comprehensive database of individual turtles, researchers can track the life history of each animal, monitor their movements, and assess their reproductive success over time. This wealth of information is invaluable for developing targeted conservation strategies and assessing the effectiveness of existing measures.
In addition to improving data collection and analysis, facial recognition technology also enhances collaboration among researchers and conservation organizations. By sharing databases and insights, scientists can work together more effectively to address the challenges facing turtle populations worldwide. This collaborative approach is essential for tackling issues such as habitat loss, climate change, and illegal poaching, which threaten the survival of many turtle species.
Despite the promising potential of AI facial recognition in turtle conservation, it is important to acknowledge the challenges and limitations associated with its implementation. High-quality images are necessary for accurate identification, which can be difficult to obtain in certain environments or with elusive species. Additionally, the initial development and deployment of these technologies require significant investment and expertise. However, as technology continues to advance and become more accessible, these barriers are likely to diminish, paving the way for broader adoption in the field of wildlife conservation.
In conclusion, AI facial recognition technology is transforming turtle research by providing a powerful tool for non-invasive monitoring and data collection. By enhancing the accuracy and efficiency of conservation efforts, this technology holds great promise for safeguarding the future of turtle populations. As researchers continue to refine and expand its applications, facial recognition is poised to play a pivotal role in the ongoing quest to protect and preserve these remarkable creatures for generations to come.
AI-Driven Solutions for Monitoring Turtle Populations
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into wildlife conservation efforts has opened new avenues for monitoring and protecting endangered species. Among these, the application of AI facial recognition technology to turtle conservation represents a significant advancement. This innovative approach addresses the challenges of traditional monitoring methods, offering a more efficient and accurate means of tracking turtle populations. As conservationists strive to protect these ancient mariners, AI-driven solutions are proving to be invaluable tools in their arsenal.
Traditionally, monitoring turtle populations has relied heavily on manual tagging and tracking, which can be labor-intensive, time-consuming, and sometimes stressful for the animals. These methods often involve capturing turtles to attach physical tags or markers, which can be invasive and may alter their natural behavior. Moreover, the vast and often inaccessible habitats of turtles, ranging from remote beaches to expansive ocean territories, make comprehensive monitoring a daunting task. In contrast, AI facial recognition technology offers a non-invasive alternative that can significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of population assessments.
Facial recognition technology, commonly associated with human identification, has been adapted to recognize individual turtles by analyzing unique patterns on their shells and faces. Each turtle possesses distinct markings, much like a human fingerprint, which can be captured and cataloged using high-resolution cameras. AI algorithms then process these images, identifying and differentiating individual turtles with remarkable precision. This method not only reduces the need for physical interaction with the animals but also allows for continuous monitoring without disturbing their natural habitats.
The implementation of AI facial recognition in turtle conservation is facilitated by advancements in machine learning and image processing. These technologies enable the rapid analysis of large datasets, allowing researchers to track population dynamics, migration patterns, and even health indicators over time. By automating the identification process, AI reduces the potential for human error and provides a scalable solution that can be applied across different regions and species. This is particularly beneficial for monitoring endangered turtle populations, where accurate data is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies.
Furthermore, AI-driven monitoring systems can be integrated with other technologies, such as satellite tracking and environmental sensors, to provide a comprehensive understanding of turtle ecosystems. This holistic approach allows conservationists to correlate turtle behavior with environmental factors, such as ocean temperature and pollution levels, offering insights into the broader impacts of climate change and human activities on marine life. By leveraging AI, researchers can make data-driven decisions to implement targeted conservation measures, such as habitat protection and restoration efforts.
Despite the promising potential of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation, challenges remain. The initial setup and maintenance of AI systems require significant investment and technical expertise, which may be a barrier for some conservation organizations. Additionally, the success of these systems depends on the availability of high-quality images and robust datasets, which can be difficult to obtain in remote or under-resourced areas. However, as technology continues to evolve and become more accessible, these obstacles are likely to diminish.
In conclusion, AI facial recognition technology represents a transformative tool in the field of turtle conservation. By providing a non-invasive, efficient, and accurate means of monitoring populations, AI enhances our ability to protect these vulnerable species. As conservationists continue to embrace AI-driven solutions, the future of turtle conservation looks increasingly promising, offering hope for the preservation of these remarkable creatures for generations to come.
Enhancing Data Accuracy in Turtle Conservation with AI
In recent years, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) into wildlife conservation efforts has opened new avenues for enhancing data accuracy and efficiency. One particularly promising application is the use of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation. This innovative approach not only streamlines the identification process but also significantly improves the precision of data collection, which is crucial for the effective management and protection of turtle populations.
Traditionally, turtle conservationists have relied on manual methods to identify individual turtles, such as tagging or photographing unique shell patterns. While these methods have been effective to some extent, they are often labor-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to human error. Moreover, the physical tagging of turtles can sometimes cause stress or harm to the animals. In contrast, AI facial recognition technology offers a non-invasive alternative that enhances the accuracy and efficiency of turtle identification.
The application of AI in this context involves training algorithms to recognize and differentiate between the unique facial features of individual turtles. By analyzing high-resolution images, AI systems can identify subtle differences in the shape, size, and pattern of a turtle’s face, much like how facial recognition technology is used in humans. This method not only reduces the likelihood of misidentification but also allows for the rapid processing of large volumes of data, which is essential for monitoring turtle populations over time.
Furthermore, the use of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation facilitates the collection of more comprehensive and reliable data. With accurate identification, researchers can track the movements, behaviors, and health of individual turtles with greater precision. This information is invaluable for understanding the dynamics of turtle populations, assessing the impact of environmental changes, and implementing targeted conservation strategies. Additionally, the ability to quickly and accurately identify turtles can aid in the detection of illegal poaching activities, thereby enhancing the protection of endangered species.
Another significant advantage of AI facial recognition technology is its potential to engage and empower local communities in conservation efforts. By providing user-friendly tools that allow individuals to contribute to data collection, AI can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility among community members. This participatory approach not only enriches the data pool but also raises awareness about the importance of turtle conservation and the role that technology can play in safeguarding biodiversity.
Despite its many benefits, the implementation of AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation is not without challenges. The development and deployment of AI systems require substantial financial investment and technical expertise, which may be beyond the reach of some conservation organizations. Moreover, the accuracy of AI algorithms depends on the quality and diversity of the training data, necessitating ongoing efforts to collect and curate comprehensive image datasets.
Nevertheless, the potential of AI facial recognition technology to transform turtle conservation is undeniable. By enhancing data accuracy and efficiency, this innovative approach can significantly improve the management and protection of turtle populations worldwide. As AI technology continues to evolve, it is likely to play an increasingly vital role in wildlife conservation, offering new tools and insights to address the complex challenges facing our planet’s biodiversity. In conclusion, the integration of AI facial recognition technology into turtle conservation represents a promising step forward in the quest to preserve these ancient and iconic creatures for future generations.
Overcoming Challenges in Turtle Conservation Using AI Technology
Turtle conservation has long been a challenging endeavor, primarily due to the difficulties in monitoring and tracking individual turtles over time. Traditional methods, such as tagging and manual identification, are labor-intensive and often intrusive, potentially causing stress to these already vulnerable creatures. However, recent advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) technology, particularly facial recognition, are offering promising solutions to these challenges. By leveraging AI, conservationists can now enhance their efforts in monitoring turtle populations more efficiently and accurately.
Facial recognition technology, commonly associated with human identification, has been adapted to recognize individual turtles by analyzing unique patterns on their shells and faces. This innovative approach allows researchers to identify and track turtles without the need for physical tags, thereby minimizing human interference. The application of AI in this context is not only non-invasive but also significantly reduces the time and resources required for data collection. Consequently, conservationists can allocate more effort towards other critical aspects of turtle conservation, such as habitat protection and public education.
Moreover, AI-driven facial recognition systems can process vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, enabling researchers to monitor large populations of turtles across different regions. This capability is particularly beneficial in areas where turtle populations are dispersed over wide geographical ranges, making traditional monitoring methods impractical. By automating the identification process, AI technology facilitates the collection of comprehensive data sets that can be used to analyze population dynamics, migration patterns, and health indicators. These insights are crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and policies.
In addition to improving data collection, AI technology also enhances the ability to detect and respond to threats facing turtle populations. For instance, by integrating facial recognition systems with real-time monitoring tools, conservationists can quickly identify and address issues such as poaching, habitat destruction, and climate change impacts. This proactive approach allows for timely interventions, potentially mitigating threats before they cause significant harm to turtle populations. Furthermore, the data generated by AI systems can be used to raise awareness and advocate for stronger conservation measures at local, national, and international levels.
Despite the numerous advantages of using AI in turtle conservation, there are challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its potential. One of the primary concerns is the accuracy of AI systems in diverse environmental conditions. Factors such as lighting, water clarity, and the presence of other marine life can affect the quality of images captured for facial recognition. To overcome these challenges, ongoing research and development are essential to refine AI algorithms and improve their robustness in varying conditions. Additionally, collaboration between technologists and conservationists is crucial to ensure that AI solutions are tailored to the specific needs of turtle conservation.
In conclusion, AI facial recognition technology represents a significant advancement in overcoming the challenges associated with turtle conservation. By providing a non-invasive, efficient, and accurate method for monitoring turtle populations, AI enhances the ability of conservationists to protect these endangered species. While challenges remain, continued innovation and collaboration hold the promise of further improving the effectiveness of conservation efforts. As AI technology continues to evolve, it is poised to play an increasingly vital role in safeguarding the future of turtles and other wildlife species.
Q&A
1. **What is AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation?**
AI facial recognition technology in turtle conservation involves using machine learning algorithms to identify and monitor individual turtles based on unique patterns on their faces or shells, similar to human facial recognition systems.
2. **How does AI facial recognition benefit turtle conservation efforts?**
AI facial recognition streamlines the process of tracking and studying turtle populations, allowing researchers to gather data more efficiently and accurately, which aids in understanding migration patterns, population dynamics, and health assessments.
3. **What challenges does AI facial recognition face in turtle conservation?**
Challenges include the need for high-quality images, variations in lighting and angles, and the development of algorithms that can accurately distinguish between individuals despite changes in appearance over time.
4. **What are the potential impacts of AI facial recognition on turtle populations?**
The technology can lead to better-informed conservation strategies, improved protection measures, and enhanced ability to monitor the effects of environmental changes and human activities on turtle populations.
5. **Which organizations are involved in using AI for turtle conservation?**
Various conservation organizations, research institutions, and technology companies collaborate to develop and implement AI facial recognition systems for turtle conservation, often supported by grants and partnerships.
6. **What future advancements are expected in AI facial recognition for turtle conservation?**
Future advancements may include improved accuracy and speed of recognition systems, integration with other monitoring technologies like drones and satellite tracking, and expanded databases for global collaboration in conservation efforts.Enhancing turtle conservation through AI facial recognition technology presents a promising advancement in wildlife management and protection efforts. By utilizing AI-driven facial recognition, researchers and conservationists can efficiently identify and monitor individual turtles, allowing for more accurate population assessments and tracking of migratory patterns. This technology facilitates the collection of critical data on turtle behavior, health, and habitat use, which can inform targeted conservation strategies and policy decisions. Additionally, AI facial recognition reduces the need for invasive tagging methods, minimizing stress and potential harm to the animals. As a result, this innovative approach not only improves the effectiveness of conservation programs but also enhances our understanding of turtle ecology, ultimately contributing to the preservation of these vital species and their ecosystems.