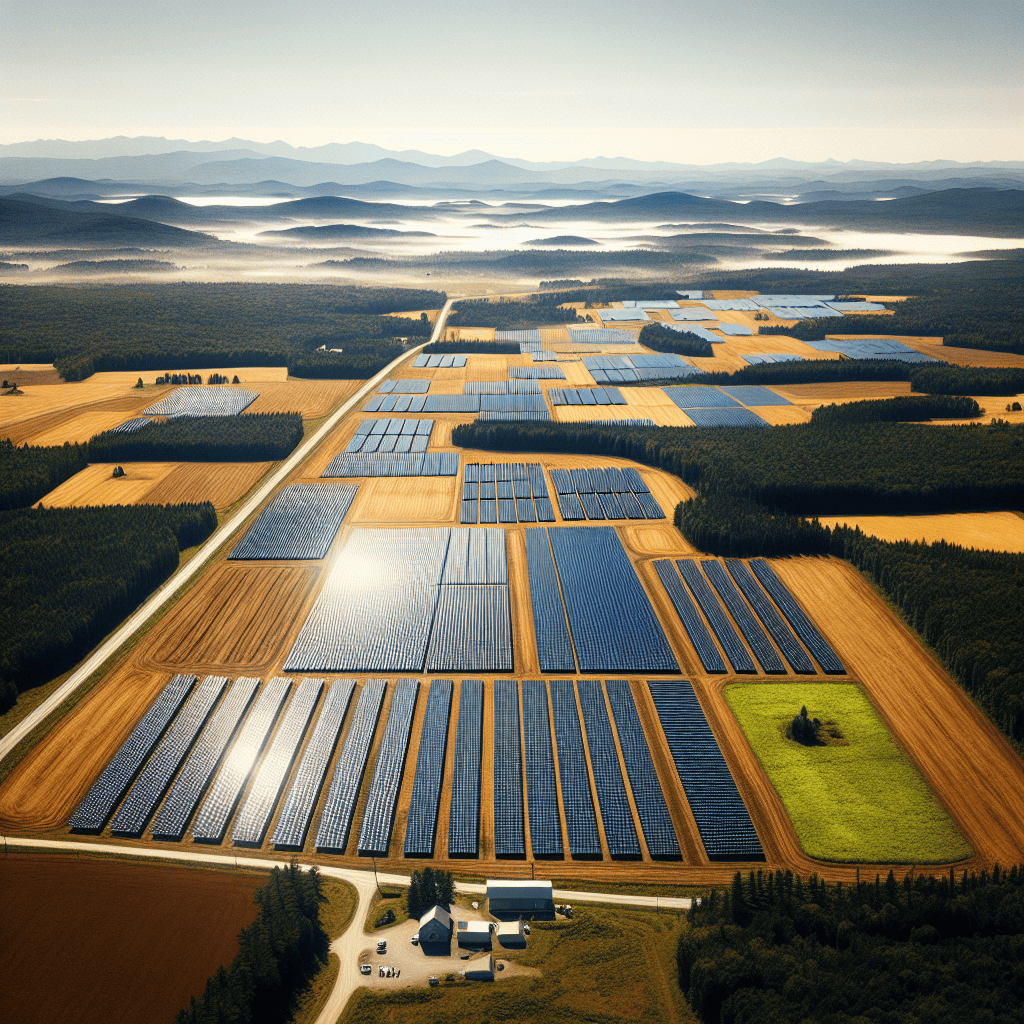
In a significant step towards sustainable energy, a 700-kW solar installation has been established on previously unused farmland in Maine, transforming the landscape and contributing to the state’s renewable energy goals. This innovative project not only optimizes land use by repurposing agricultural space for clean energy generation but also supports local economies and reduces carbon emissions. By harnessing the abundant sunlight in the region, the solar installation is set to provide power to hundreds of homes, demonstrating the potential of solar energy to revitalize rural areas while promoting environmental stewardship. As Maine continues to embrace renewable energy solutions, this solar project serves as a model for similar initiatives across the country, showcasing the benefits of integrating solar technology into agricultural settings.
Economic Benefits of 700-kW Solar Installations in Maine
The economic benefits of a 700-kW solar installation in Maine are multifaceted, impacting not only the immediate area but also contributing to broader state and national goals regarding renewable energy and sustainability. As Maine continues to explore innovative ways to harness its natural resources, the conversion of unused farmland into solar energy sites represents a significant opportunity for economic growth. This transformation not only optimizes land use but also generates substantial financial returns for local communities and stakeholders.
One of the most immediate economic advantages of a 700-kW solar installation is the creation of jobs. The construction phase of such a project typically requires a diverse workforce, including engineers, electricians, and laborers. This influx of employment opportunities can stimulate the local economy, providing jobs for residents and supporting local businesses that supply materials and services. Furthermore, once the installation is operational, it necessitates ongoing maintenance and monitoring, which can lead to additional long-term employment opportunities in the region.
In addition to job creation, solar installations can significantly reduce energy costs for local businesses and residents. By generating clean, renewable energy, these systems can lower electricity bills, allowing businesses to allocate resources to other critical areas such as expansion or employee wages. This reduction in energy costs can be particularly beneficial for agricultural operations, which often face high energy expenses. By utilizing solar energy, farmers can enhance their profitability while simultaneously contributing to a more sustainable energy future.
Moreover, the economic impact of solar installations extends to property values. Studies have shown that properties equipped with solar energy systems often experience an increase in value. This trend can be particularly advantageous for landowners who lease their land for solar development, as they can receive a steady stream of income while maintaining ownership of their property. This arrangement not only provides financial stability for landowners but also encourages the responsible use of agricultural land, preventing it from falling into disuse or being developed for less sustainable purposes.
The tax incentives and rebates associated with solar energy projects further enhance their economic viability. In Maine, various state and federal programs offer financial incentives for solar installations, making it more feasible for developers to invest in renewable energy. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront costs associated with solar projects, allowing for quicker returns on investment. As a result, the economic landscape becomes more favorable for both investors and local governments, which can benefit from increased tax revenues generated by solar facilities.
Additionally, the shift towards renewable energy sources like solar power aligns with Maine’s broader economic goals of sustainability and resilience. By investing in solar energy, the state can reduce its dependence on fossil fuels, thereby enhancing energy security and stability. This transition not only supports local economies but also positions Maine as a leader in the renewable energy sector, attracting further investment and innovation.
In conclusion, the economic benefits of a 700-kW solar installation in Maine are substantial and far-reaching. From job creation and reduced energy costs to increased property values and tax incentives, the advantages extend beyond the immediate financial returns. As Maine continues to embrace renewable energy, the transformation of unused farmland into solar installations serves as a model for sustainable economic development, demonstrating how innovative approaches can yield significant benefits for communities and the environment alike.
Environmental Impact of Utilizing Unused Farmland for Solar Energy
The environmental impact of utilizing unused farmland for solar energy is a topic of increasing relevance as society seeks sustainable solutions to meet its energy demands. In Maine, the recent installation of a 700-kW solar array on previously unproductive agricultural land exemplifies how such initiatives can yield significant ecological benefits while promoting renewable energy. By transforming these underutilized spaces into productive solar farms, communities can harness the sun’s power without compromising the integrity of more fertile agricultural areas.
One of the primary advantages of deploying solar installations on unused farmland is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. Traditional energy sources, such as fossil fuels, contribute significantly to climate change through the release of carbon dioxide and other harmful pollutants. In contrast, solar energy generation produces no direct emissions, thereby mitigating the overall carbon footprint associated with energy consumption. By converting barren land into solar farms, Maine is taking a proactive step toward reducing its reliance on fossil fuels and promoting cleaner energy alternatives.
Moreover, the use of unused farmland for solar energy can enhance biodiversity. Often, agricultural practices can lead to habitat destruction and a decline in local flora and fauna. However, solar installations can coexist with natural ecosystems, allowing for the preservation of local wildlife. In many cases, solar farms can be designed to incorporate native vegetation, which not only supports local biodiversity but also improves soil health and reduces erosion. This dual benefit of energy production and ecological preservation underscores the potential for solar energy to contribute positively to the environment.
In addition to promoting biodiversity, solar installations on unused farmland can also improve land management practices. By repurposing land that is not suitable for traditional agriculture, communities can avoid the pressures of land conversion that often lead to deforestation and habitat loss. This strategic use of land helps maintain the ecological balance while providing a sustainable energy source. Furthermore, the installation of solar panels can create a buffer against soil degradation, as the land beneath the panels is often left undisturbed, allowing for natural processes to continue.
Transitioning to solar energy on unused farmland also has implications for water conservation. Traditional agricultural practices can be water-intensive, leading to depletion of local water resources. In contrast, solar farms require minimal water for maintenance, primarily for cleaning the panels. This reduced water usage can alleviate stress on local water supplies, particularly in regions where water scarcity is a concern. By prioritizing solar energy development on less productive land, Maine is not only addressing its energy needs but also promoting responsible water management practices.
Furthermore, the economic benefits of solar installations cannot be overlooked. By investing in renewable energy, communities can create jobs in installation, maintenance, and operation, contributing to local economies. The revenue generated from solar energy can also provide funding for community projects and infrastructure improvements, further enhancing the quality of life for residents.
In conclusion, the environmental impact of utilizing unused farmland for solar energy is multifaceted, encompassing reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, enhancements to biodiversity, improved land management, water conservation, and economic growth. The 700-kW solar installation in Maine serves as a model for how communities can effectively harness renewable energy while simultaneously promoting ecological sustainability. As the world continues to grapple with the challenges of climate change and resource depletion, initiatives like this highlight the potential for innovative solutions that benefit both the environment and society.
Case Study: Successful 700-kW Solar Projects in Maine

In recent years, Maine has emerged as a leader in renewable energy initiatives, particularly in the realm of solar power. A notable example of this trend is the successful installation of a 700-kW solar project that has transformed previously unused farmland into a productive energy-generating site. This case study not only highlights the potential of solar energy in rural areas but also underscores the benefits of repurposing agricultural land for sustainable energy production.
The project, which was developed in collaboration with local stakeholders, showcases how innovative approaches can revitalize underutilized spaces while contributing to the state’s energy goals. By converting farmland that had been lying fallow into a solar array, the initiative demonstrates a dual benefit: it generates clean energy and preserves the agricultural landscape. This transformation is particularly significant in Maine, where the agricultural sector plays a vital role in the economy and community identity.
Moreover, the 700-kW solar installation is designed to produce enough electricity to power approximately 100 homes annually. This capacity not only contributes to the local grid but also supports Maine’s commitment to increasing its renewable energy portfolio. As the state aims to achieve 80% renewable energy by 2030, projects like this one are essential in meeting those ambitious targets. The integration of solar power into the energy mix is a crucial step toward reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.
In addition to environmental benefits, the project has also created economic opportunities for the local community. The construction and maintenance of the solar array have generated jobs, providing employment for local workers and stimulating the economy. Furthermore, the project has the potential to offer financial incentives to the landowners involved, allowing them to diversify their income streams while maintaining their connection to agriculture. This aspect is particularly important in rural areas, where economic diversification can enhance community resilience.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable practices. As more individuals and businesses seek to reduce their carbon footprints, the availability of locally generated solar power becomes increasingly attractive. The 700-kW installation not only meets this demand but also serves as a model for future projects across the state. By demonstrating the feasibility and benefits of solar energy on agricultural land, it paves the way for similar initiatives that can further enhance Maine’s renewable energy landscape.
Furthermore, the project has garnered support from various stakeholders, including government agencies, environmental organizations, and community members. This collaborative approach has been instrumental in overcoming potential challenges, such as zoning regulations and land use concerns. By engaging with the community and addressing their needs, the project has fostered a sense of ownership and pride among residents, reinforcing the idea that renewable energy development can be a community-driven effort.
In conclusion, the successful 700-kW solar installation in Maine exemplifies the transformative potential of solar energy in repurposing unused farmland. By generating clean energy, creating jobs, and fostering community engagement, this project not only contributes to the state’s renewable energy goals but also serves as a blueprint for future initiatives. As Maine continues to embrace sustainable practices, the lessons learned from this case study will undoubtedly inspire further advancements in solar energy development across the region.
Community Reactions to Solar Installations on Farmland
The installation of a 700-kW solar array on previously unused farmland in Maine has sparked a variety of reactions from the local community, reflecting a complex interplay of environmental, economic, and social considerations. As renewable energy initiatives gain momentum across the United States, the transformation of agricultural land into solar farms often elicits both enthusiasm and concern among residents. In this case, the community’s response has been shaped by a range of factors, including the perceived benefits of clean energy, the potential impact on local agriculture, and the broader implications for land use in the region.
Many community members have expressed strong support for the solar installation, viewing it as a progressive step toward sustainability. Proponents argue that harnessing solar energy not only contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions but also aligns with Maine’s commitment to increasing renewable energy sources. The installation is seen as a vital component in the fight against climate change, providing a clean alternative to fossil fuels while promoting energy independence. Furthermore, supporters highlight the potential for job creation during the construction and maintenance phases of the solar project, which could provide a much-needed economic boost to the local area.
Conversely, some residents have voiced concerns regarding the conversion of farmland into solar energy production sites. For these individuals, the loss of agricultural land raises questions about food security and the long-term viability of local farming. They worry that prioritizing solar installations over traditional agriculture could set a precedent that undermines the region’s agricultural heritage. This sentiment is particularly strong among farmers who fear that the encroachment of solar farms may limit their ability to expand or sustain their operations. As a result, discussions surrounding land use have become increasingly nuanced, with community members advocating for a balanced approach that considers both renewable energy development and agricultural preservation.
In addition to environmental and agricultural concerns, the community’s reaction has also been influenced by the economic implications of the solar installation. While many residents appreciate the potential for lower energy costs and increased tax revenue from the solar project, others are apprehensive about the long-term economic impact on local property values. Some fear that the presence of solar farms may deter potential buyers who prefer traditional agricultural landscapes, thereby affecting the overall desirability of the area. This concern has led to calls for transparency and dialogue between solar developers and community members to ensure that the benefits of the project are equitably distributed.
Moreover, the installation has prompted discussions about the future of land use in Maine, particularly as the state grapples with the dual challenges of climate change and agricultural sustainability. Community forums and public meetings have become platforms for residents to voice their opinions, share their experiences, and engage in constructive dialogue about the best path forward. These conversations have underscored the importance of collaboration among stakeholders, including local government, farmers, and renewable energy advocates, to develop strategies that honor both the need for clean energy and the preservation of agricultural land.
In conclusion, the community reactions to the 700-kW solar installation on unused farmland in Maine illustrate the multifaceted nature of renewable energy development. While many residents celebrate the environmental benefits and economic opportunities presented by solar energy, others remain cautious about the implications for agriculture and land use. As the community navigates these complex issues, it is clear that ongoing dialogue and collaboration will be essential in finding a harmonious balance between advancing renewable energy initiatives and preserving the region’s agricultural legacy.
The Future of Renewable Energy in Maine’s Agricultural Sector
The future of renewable energy in Maine’s agricultural sector is poised for significant transformation, particularly as innovative projects like the 700-kW solar installation on previously unused farmland demonstrate the potential for synergy between agriculture and renewable energy. This initiative not only highlights the feasibility of integrating solar power into agricultural landscapes but also serves as a model for sustainable practices that can benefit both farmers and the environment. As Maine grapples with the challenges of climate change and seeks to reduce its carbon footprint, the agricultural sector stands at a crossroads where traditional practices can be enhanced through the adoption of renewable energy technologies.
The integration of solar energy into farming operations offers numerous advantages, including the potential for increased revenue streams for farmers. By utilizing land that may otherwise remain fallow, farmers can generate income from solar leases while maintaining their agricultural activities. This dual-use approach not only maximizes land productivity but also contributes to the state’s renewable energy goals. As Maine aims to achieve 100% renewable energy by 2050, projects like the 700-kW solar installation exemplify how agricultural land can play a pivotal role in this transition.
Moreover, the environmental benefits of solar installations are significant. By harnessing the sun’s energy, these projects reduce reliance on fossil fuels, thereby decreasing greenhouse gas emissions and mitigating the impacts of climate change. In a state like Maine, where agriculture is a vital part of the economy, the adoption of renewable energy can help farmers adapt to changing climatic conditions. For instance, solar energy can power irrigation systems, reducing the need for diesel generators and lowering operational costs. This not only enhances the sustainability of farming practices but also ensures that farmers can remain competitive in an evolving market.
Transitioning to renewable energy sources also aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable products. As more consumers prioritize environmentally friendly practices, farmers who invest in solar energy can market their products as part of a broader commitment to sustainability. This trend is particularly relevant in Maine, where local food movements and organic farming practices are gaining traction. By showcasing their use of renewable energy, farmers can attract environmentally conscious consumers, thereby enhancing their marketability and potentially increasing their profits.
Furthermore, the collaboration between agricultural stakeholders and renewable energy developers is essential for the successful implementation of such projects. Engaging local communities, agricultural organizations, and policymakers in discussions about the benefits and challenges of solar installations can foster a supportive environment for renewable energy initiatives. By addressing concerns related to land use, aesthetics, and potential impacts on farming operations, stakeholders can work together to create solutions that benefit all parties involved.
In conclusion, the future of renewable energy in Maine’s agricultural sector is bright, particularly as demonstrated by the successful implementation of solar projects on unused farmland. This innovative approach not only provides farmers with new revenue opportunities but also contributes to the state’s broader environmental goals. As Maine continues to explore the intersection of agriculture and renewable energy, it is clear that such initiatives will play a crucial role in shaping a sustainable and resilient agricultural landscape. By embracing these changes, Maine can lead the way in demonstrating how agriculture and renewable energy can coexist harmoniously, paving the path for a greener future.
Technical Aspects of Implementing 700-kW Solar Systems on Farmland
The implementation of a 700-kW solar installation on previously unused farmland in Maine represents a significant advancement in the integration of renewable energy solutions within agricultural landscapes. This project not only highlights the potential for solar energy to contribute to local economies but also emphasizes the technical considerations necessary for successfully deploying such systems in rural settings. The process begins with a thorough site assessment, which is crucial for determining the suitability of the land for solar development. Factors such as soil stability, topography, and existing vegetation must be evaluated to ensure that the installation will not only be efficient but also environmentally sustainable.
Once the site is deemed appropriate, the next step involves designing the solar array. This includes selecting the type of solar panels, inverters, and mounting systems that will be used. In the case of a 700-kW system, high-efficiency photovoltaic (PV) panels are typically chosen to maximize energy output while minimizing the physical footprint. The design phase also incorporates considerations for the orientation and tilt of the panels, as these factors significantly influence the amount of sunlight captured throughout the year. By optimizing these parameters, the system can achieve peak performance, generating substantial amounts of electricity.
Following the design phase, the installation process begins, which requires careful coordination among various stakeholders, including engineers, contractors, and local authorities. The construction of the solar array involves site preparation, which may include grading the land and installing necessary infrastructure such as access roads and electrical connections. During this phase, it is essential to adhere to local regulations and environmental guidelines to mitigate any potential impacts on the surrounding ecosystem. For instance, erosion control measures may be implemented to prevent soil degradation, ensuring that the land remains viable for agricultural use in the future.
Once the physical installation is complete, the next critical step is the integration of the solar system with the local electrical grid. This process involves working closely with utility companies to ensure that the generated electricity can be effectively distributed. The installation of inverters is particularly important, as these devices convert the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC), which is compatible with the grid. Additionally, advanced monitoring systems are often installed to track the performance of the solar array, allowing for real-time data analysis and maintenance planning.
Moreover, the implementation of a 700-kW solar system on farmland necessitates ongoing maintenance and management to ensure optimal performance over its lifespan. Regular inspections and cleaning of the solar panels are essential to prevent the accumulation of dirt and debris, which can hinder energy production. Furthermore, the integration of smart technology can enhance operational efficiency by providing insights into energy usage patterns and enabling predictive maintenance.
In conclusion, the technical aspects of implementing a 700-kW solar installation on farmland in Maine encompass a multifaceted approach that includes site assessment, design, construction, integration with the electrical grid, and ongoing maintenance. This comprehensive process not only transforms unused agricultural land into a productive energy source but also sets a precedent for future renewable energy projects in rural areas. By embracing such innovative solutions, communities can harness the power of solar energy while promoting sustainable agricultural practices, ultimately contributing to a greener and more resilient future.
Q&A
1. **What is the capacity of the solar installation in Maine?**
The solar installation has a capacity of 700 kW.
2. **What type of land is being used for the solar installation?**
The installation is transforming unused farmland.
3. **What are the environmental benefits of the solar installation?**
The installation helps reduce carbon emissions and promotes renewable energy use.
4. **How does the solar installation impact local agriculture?**
It utilizes previously unused land, potentially allowing for dual land use with agriculture and energy production.
5. **What is the expected output of the 700-kW solar installation?**
The installation is expected to generate a significant amount of clean energy, enough to power hundreds of homes.
6. **Who is involved in the development of the solar installation?**
The project typically involves local government, energy companies, and possibly community stakeholders.The 700-kW solar installation in Maine represents a significant transformation of previously unused farmland into a productive renewable energy source. This project not only optimizes land use by converting non-arable areas into a sustainable energy generation site but also contributes to the state’s goals for clean energy and carbon reduction. By harnessing solar power, the installation supports local energy needs, reduces reliance on fossil fuels, and promotes environmental stewardship. Additionally, it serves as a model for similar initiatives, demonstrating that agricultural land can be repurposed for renewable energy without compromising future agricultural potential. Overall, this solar project exemplifies the intersection of sustainable development and innovative land management, paving the way for a greener future while benefiting the local economy and community.